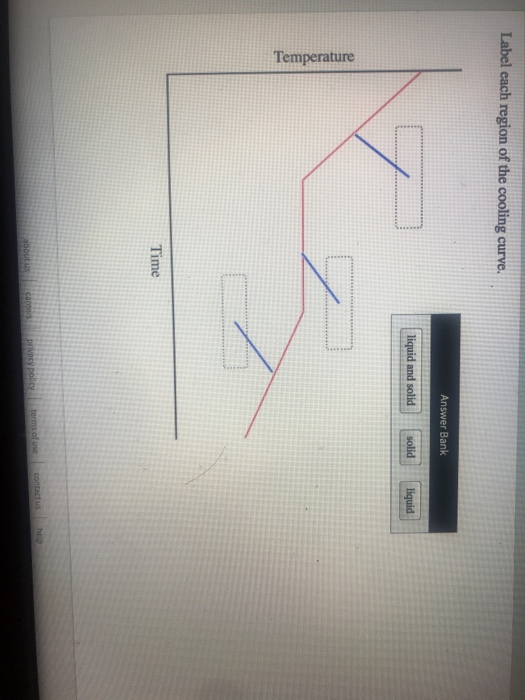
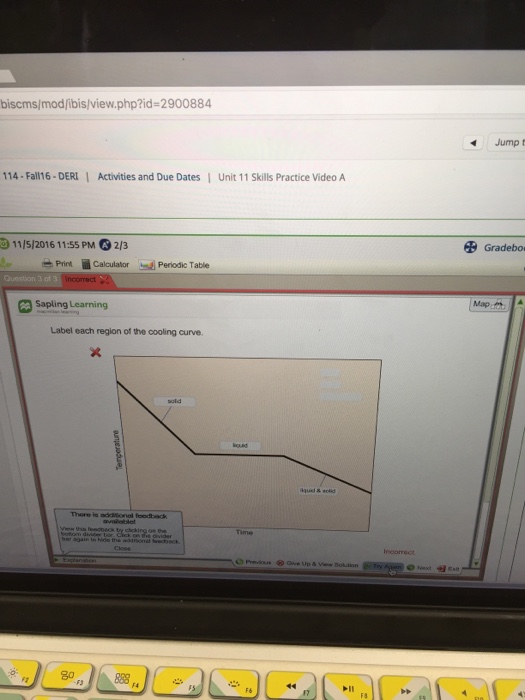
Label Each Region of the Cooling Curve.
Boiling point of SO2. Liquid water becomes water vapor or steam when it enters the gaseous phase.
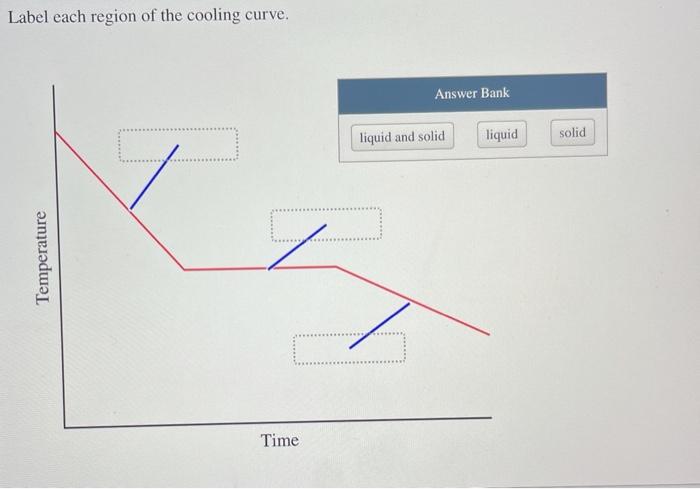
Solved Label Each Region Of The Cooling Curve Answer Bank Chegg Com
Heating curves show how the temperature changes as a substance is heated up.

. Cooling curve worksheets showing all 8 printables. Up to 24 cash back On the heating curve diagram provided above label each of the following regions. They show how the temperature changes as a substance is cooled down.
Heating cooling curves worksheet. Up to 24 cash back 1 Define temperature and heat and give the appropriate unit for each. In this experiment the cooling curve method similar to but simpler than DTA in that it does not.
Imagine that you have a block of ice that is at a temperature of -30C well below its melting point. The following physical data may be helpful. Eutectic matrix consisting of dark lead-rich regions and light tin-rich regions.
Carefully read the procedure directions below and make a useful and organized data table for this lab. Label each sample immediately to avoid mixing them up. Q mCH2OgΔT q m C H 2 O g Δ T where m is the mass of the sample of water.
C For section RS of the graph state what is happening to the water molecules as heat is added. Determine the meltingfreezing point and boilingcondensing point from a heating or cooling curve. Sketch the simplest phase diagram consistent with.
A Liquidus 2900 C b Solidus 2710 C c Freezing range 29002710 190C d Pouring temperature 2990 C e Superheat 29902900 90C f Local Solidification time 34040 300 s g Total solidification time 340 s h Nb 60 wt W 11-23 The coppersilver phase diagram is shown in Figure 1130. Appropriate and with equal intervals. Liquid only Gas only Phase change For section QR of the graph state what is happening to the water molecules as heat is addqd HE empe For section aof the graph state what is happening to the water molecules as heat is added.
A On the heating curve diagram provided above label each of the following regions. At each region of the curve plateau or diagonal labelthe states of matter present. A On the heating curve diagram provided above label each of the following regions.
Thermal energy is needed to overcome the forces. Different substances have different melting points and boiling points but the shapes of their heating curves are very similar. It represents the heating of substance X at a constant rate of heat transfer.
The solid-liquid curve labeled BD shows the temperatures and pressures at which ice and liquid water are in equilibrium representing the meltingfreezing points for water. Just like heating curves cooling curves have horizontal flat parts where the state changes from gas to liquid or from liquid to solid. Please help me solve this question with an understanding.
Region DE This region represents a mixture of liquid and vapour. Label each region of the. 1 a low temperature plateau relatively flat slope 2 a region of temperature change steeper slope 3 a high temperature plateau relatively flat slope Attach your DATA TABLE and your scatterplot of your heating curve on graph paper.
Then divide your heating curve into three regions. Examine the heating curve of water and determine what is happening at each stage. The ice is in a closed container.
This region represents the liquid state water. See the answer See the answer done loading. Surroundings over time be sure to label your axes.
Au and Sb melt at 1060C and 630C respectively and form one compound AuSb 3 which melts incongruently at 800C. Heating cooling curve 4. I dont know where to begin and what is the concept behind it.
Write a short explanation for your prediction 3. Think carefully about any changes in gradient that occur. Use the heat of vaporization ΔHvap Δ H v a p to calculate how much heat was absorbed in this process.
Im so stuck on it. Cooling Curves Heating curves show how the temperature changes as a substance is heated up. Label each graph as heating curve and cooling curve10 Temperature oC Heating and Cooling Curves of Water 1000900800Heating curve 700600500400Cooling curve 300200100Optional.
Line drawn to determine the gradient0005101520253035Time minutes Scales on both axes. Make sure you use a different colour or symbol for each type of chocolate. As heat is steadily added to the ice block the water molecules will begin to vibrate faster and faster as they absorb kinetic energy.
Note that this curve exhibits a slight negative slope greatly exaggerated for clarity indicating that the melting point for water decreases slightly as pressure increases. The red regions indicate where the material is liquid the blue regions indicate where the material is solid and the green regions indicate where the solid and liquid phases are in equilibrium. Label the region of each curve when the chocolates were freezing.
Make a hypothesis a proposed explanation for an observation. Cooling curves are the opposite. Liquid only Gas only Phase change b For section QR of the graph state what is happening to the water molecules as heat is added.
Use the same colour as you did when plotting the data. Label the phase regions and draw cooling curves for melts containing 40 K 55 K and 90 K. Students compare illustrations of each physical state depicted on the curve.
Draw a smooth curve of best fit for each chocolate. Below are cooling curves for the same system recorded for different compositions and then displaced along the time axis. Spanish Worksheets For Kids.
For example this is the heating curve for iron a metal that melts at 1538C and boils at 2861C. Note that it might not be possible to weigh out these granular. Up to 24 cash back a On the heating curve diagram provided above label each of the following regions.
A Did the H 2. On your paper draw the cooling curve for SO2 starting at -50 C andending at -100 C. Indicate the phases appearing or disappearing at each break or halt.
Cooling curves are the opposite. Redraw all graphs and label them. Worksheet- Heating Curve of WaterCalculations Involving Phase Changes Write all answers on your own answer sheet.
Make a data table. Make sure you have appropriate titles and use units. 2 Describe and graph the temperature changes for a heating or cooling curve and label each part of the curve with the appropriate phases.
There is a gain in both potential energy and kinetic energy therefore the temperature rises and the distance between individual molecules increases and they move faster.
Solved On Sos 2 At A Resting Pulse Rate Of 77 Beats Per Chegg Com

Heating And Cooling Curves Also Called Temperature Curves Chemistry For Non Majors
Solved Label Each Region Of Thecooling Curve Please Help Me Chegg Com
0 Response to "Label Each Region of the Cooling Curve."
Post a Comment